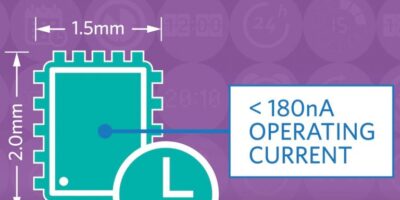
The battery life of space-constrained systems such as wearables, medical monitors, point-of-sale (PoS) equipment and portable terminals can be extended, says Maxim Integrated, using the MAX31341B.
Power
Varta announces rechargeable batteries for hearing aids
Rechargeable Lithium-ion batteries with a high-energy density and capacity will be unveiled at the Wearable Technologies Conference in San Francisco for wearables and hearables (hearing aids, over-ear headphones and wireless telephony ear buds).
Wearable Technology Takes Advantage of Low Power Conversion in Health and Wellbeing
Once as simple as a walking or running step counter – or pedometer – wearable devices have become more advanced – or smart – seemingly overnight. From vibration-from-speech generating vests for the deaf to Google Glass to advanced fitness activity trackers to night vision equipment and even heads-up imaging displays, wearable devices have become a part of the mainstream consumer, military, and industrial markets. A “wearable” can be defined as a product that is worn by the user for an extended period of time and in some way, enhances the user’s experience as a result of the product being worn. A “smart” wearable adds connectivity and independent data processing capability to the device. Wearables are divided into four application sub-categories: fitness/wellness (activity monitors, fitness bands, foot pods and heart rate monitors), infotainment (smart glasses/goggles, smart watches and imaging devices), military (night vision equipment, heads-up displays, exo-skeletons and smart clothing), and industrial (body-worn terminals) [Source: IHS Electronics and Media, 2013]. These categories have different market forces driving their adoption rates. For military, it’s the desire to improve situational awareness, maps/routes, combat efficiency and save lives. For industrial, the main drivers are improving production line efficiency and tracking capability. For infotainment, it’s the continually exploding gaming market with cutting edge imaging and virtual reality, as well as the increasing number of devices able to connect wirelessly to smart phones to become part of the “internet of things” (IoT). Finally, for the wellness and medical segments, the key driving forces include: rising life expectancy, curtailing escalating medical and insurance costs, the desire to prolong a healthy life and to reduce hospital stays.
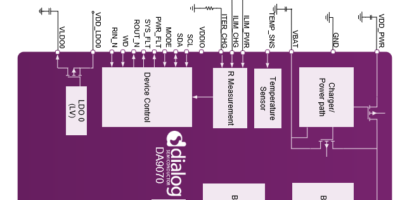
Nanopower PMICs extend battery life for IoT applications
Two integrated nanopower PMICs for IoT applications, the DA9070 and DA9073, have been released by Dialog. The PMICs are designed for ‘always-on’ IoT devices such as fitness trackers, smartwatches and smart home products which are expected to spend less time tethered to a charger, while expanding feature sets present new challenges to battery life.
About Weartech
This news story is brought to you by weartechdesign.com, the specialist site dedicated to delivering information about what’s new in the wearable electronics industry, with daily news updates, new products and industry news. To stay up-to-date, register to receive our weekly newsletters and keep yourself informed on the latest technology news and new products from around the globe. Simply click this link to register here: weartechdesign.com