Integrated IP and software develop contextually-aware IoT devices
At CES this week, Ceva will demonstrate its SenslinQ integrated hardware IP and software platform, designed to streamline the development of contextually-aware IoT devices.
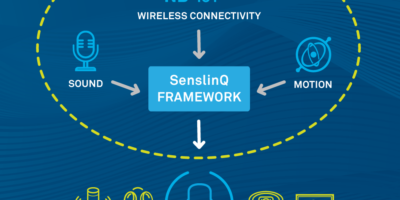
The platform collects, processes and links data from multiple sensors to enable intelligent devices to understand their surroundings, explains the company by aggregating sensor fusion, sound and connectivity technologies.
Contextual awareness adds value and enhances the user experience of smartphones, laptops, augmented reality/virtual reality (AR/VR) headsets, robots, hearables and wearables. The SenslinQ platform centralises the workloads that require an intimate understanding of the physical behaviours and anomalies of sensors. It collects data from multiple sensors within a device, including microphones, radars, inertial measurement units (IMUs), environmental sensors, and time of flight (ToF) sensors, and conducts front-end signal processing such as noise suppression and filtering on this data. It applies algorithms to create “context enablers” such as activity classification, voice and sound detection, and presence and proximity detection. These context enablers can be fused on a device or sent wirelessly via Bluetooth, Wi-Fi or NB-IoT, to a local edge computer or the cloud to determine and adapt the device to its environment.
The customisable hardware reference design is composed of an Arm or RISC-V microcontroller, CEVA-BX DSPs and a wireless connectivity island, such as RivieraWaves Bluetooth, wi-fi or Dragonfly NB-IoT platforms, or other connectivity standards provided by the customer or third parties. Each components of these three components are connected using standard system interfaces.
The SenslinQ software is comprised of a portfolio of ready-to-use software libraries from CEVA and its ecosystem partners. Libraries include the Hillcrest Labs MotionEngine software packages for sensor fusion and activity classification in mobile, wearables and robots, the ClearVox front-end voice processing, WhisPro speech recognition and DSP and artificial intelligence (AI) libraries. There is also third party software components for active noise cancellation (ANC), sound sensing and 3D audio.
The accompanying SenslinQ framework is a Linux-based hardware abstraction layer (HAL) reference code and application programming interfaces (APIs) for data and control exchange between the multiple processors and sensors.