Toshiba has announced the release of a new series of low-dropout (LDO) voltage regulators in their ultra-miniature DFN4D package type.
IoT
Arrow Edge AI engineering services launches to boost support for advanced device development
Arrow Electronics is strengthening support for customers seeking to accelerate their embedded applications with artificial intelligence and machine learning by launching Arrow Edge AI engineering services. The resources include engineering consultancy, technical training, design services, ready-to-use software, and a curated selection of vendor-specific and independent tools.
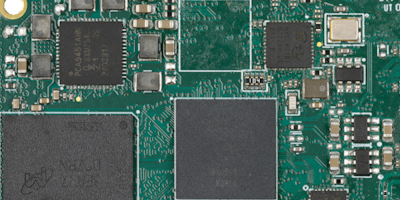
SoM by Variscite brings machine learning to compact, cost-optimised, rugged edge devices
Variscite has announced the newest member of the DART Pin2Pin family for machine learning on edge devices for markets like industrial, IoT, smart devices, and wearables.
Panasonic introduces new Amorton indoor solar cell series
Panasonic’s hydrogenated amorphous silicon (a-Si:H) solar cells, known as Amorton, power indoor and outdoor applications like IoT devices, watches, sensor nodes, asset trackers, or remote controls. Amorton can harvest energy reliably and sustainably even in low light and artificial light environments.
About Weartech
This news story is brought to you by weartechdesign.com, the specialist site dedicated to delivering information about what’s new in the wearable electronics industry, with daily news updates, new products and industry news. To stay up-to-date, register to receive our weekly newsletters and keep yourself informed on the latest technology news and new products from around the globe. Simply click this link to register here: weartechdesign.com